
Children's literature or juvenile literature:includes stories, books, magazines, and poems that are enjoyed by children. Modern children's literature is classified in two different ways: genre or the intended age of the reader.
The development of early children's literature, before printing was invented, is difficult to trace. Even after printing became widespread, many classic "children's" tales were originally created for adults and later adapted for a younger audience. Since the 15th century, a large quantity of literature, often with a moral or religious message, has been aimed specifically at children. The late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries became known as the "Golden Age of Children's Literature" as this period included the publication of many books acknowledged today as classics.

Aesop:an Ancient Greek fabulist or story teller credited with a number of fables now collectively known as Aesop's Fables. Although his existence remains uncertain and no writings by him survive, numerous tales credited to him were gathered across the centuries and in many languages in a storytelling tradition that continues to this day. Many of the tales are characterized by animals and inanimate objects that speak, solve problems, and generally have human characteristics.

The Brothers Grimm:Jacob (1785–1863) and Wilhelm Grimm (1786–1859), were German academics, philologists, cultural researchers, lexicographers and authors who together specialized in collecting and publishing folklore during the 19th century. Their first collection of folk tales, Children's and Household Tales (Kinder- und Hausmärchen), was published in 1812.

Hans Christian Andersen:a Danish author. Although a prolific writer of plays, travelogues, novels, and poems, Andersen is best remembered for his fairy tales. Andersen's popularity is not limited to children; his stories, called eventyr in Danish, express themes that transcend age and nationality.
Andersen's fairy tales, which have been translated into more than 125 languages, have become culturally embedded in the West's collective consciousness, readily accessible to children. Some of his most famous fairy tales include "The Emperor's New Clothes", "The Little Mermaid", "The Nightingale", "The Snow Queen", "The Ugly Duckling", "Thumbelina", and many more.
His stories have inspired ballets, animated and live-action films, and plays.

A fable differs from a parable in that the latter excludes animals, plants, inanimate objects, and forces of nature as actors that assume speech or other powers of humankind.
Usage has not always been so clearly distinguished. In the King James Version of the New Testament, "mythos" was rendered by the translators as "fable" in the First Epistle to Timothy, the Second Epistle to Timothy, the Epistle to Titus and the First Epistle of Peter.
Readers Theatre or Reader's Theater:a style of theater in which the actors do not memorize their lines. Actors use only vocal expression to help the audience understand the story rather than visual storytelling such as sets, costumes, intricate blocking, and movement. This style of performance of literature was initially lauded because it emphasized hearing a written text as a new way to understand literature.

Alan Alexander Milne:an English author, best known for his books about the teddy bear Winnie-the-Pooh and for various poems. Milne was a noted writer, primarily as a playwright, before the huge success of Pooh overshadowed all his previous work. Milne served in both World Wars, joining the British Army in World War I, and was a captain of the British Home Guard in World War II.

Winnie-the-Pooh, also called Pooh Bear:a fictional anthropomorphic teddy bear created by English author A. A. Milne. The first collection of stories about the character was the book Winnie-the-Pooh (1926), and this was followed by The House at Pooh Corner (1928).
Main characters in Wimmie- the-Pooh

Pooh:naive and slow-witted, but he is also friendly, thoughtful, and steadfast. Although he and his friends agree that he "has no Brain", Pooh is occasionally acknowledged to have a clever idea, usually driven by common sense.
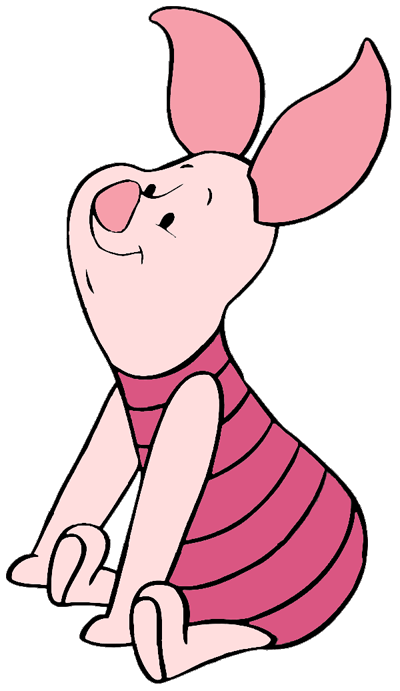
Piglet:Winnie‑the‑Pooh's closest friend amongst all the toys/animals featured in the stories. Despite the fact that he is a "Very Small Animal" of a generally timid disposition, he tries to be brave and on occasion conquers his fears.

Eeyore:He is generally characterized as a pessimistic, gloomy, depressed, anhedonic, old grey stuffed donkey who is a friend of the title character, Winnie-the-Pooh.

Tigger:with distinctive orange and black stripes, large eyes, a long chin, a springy tail, and (the one detail originating from A. A. Milne) his love of bouncing. As he says himself, "Bouncing is what Tiggers do best."
Rabbit:He is a friend of Winnie–the–Pooh, regards himself as practical and tends to take the lead, though not always with the results that he intends.
Christopher Robin:named after Christopher Robin Milne, the author's son. Christopher Robin is cheerful, compassionate, adventurous, fun-loving, imaginative, and helpful. Despite being a child, he is much wiser and more mature than many of the other characters, and is someone Pooh and the others look up to. In the book illustrations, his house appears as a hollow tree with a door at the top of the forest.

The Hundred Acre Wood:based on the real-life Five Hundred Acre Wood in Ashdown Forest, is a part of the land inhabited by Winnie-the-Pooh and his friends in the Winnie-the-Pooh series of children's stories by author A. A. Milne. The wood is visited regularly by the young boy Christopher Robin, who accompanies Pooh and company on their many adventures.

Sir James Matthew Barrie, 1st Baronet:a Scottish novelist and playwright, best remembered today as the creator of Peter Pan.

Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle KStJ, DL:a Scottish writer and physician, most noted for creating the fictional detective Sherlock Holmes and writing stories about him which are generally considered milestones in the field of crime fiction.
He is also known for writing the fictional adventures of a second character he invented, Professor Challenger, and for popularising the mystery of the Mary Celeste. He was a prolific writer whose other works include fantasy and science fiction stories, plays, romances, poetry, non-fiction and historical novels.
沒有留言:
張貼留言